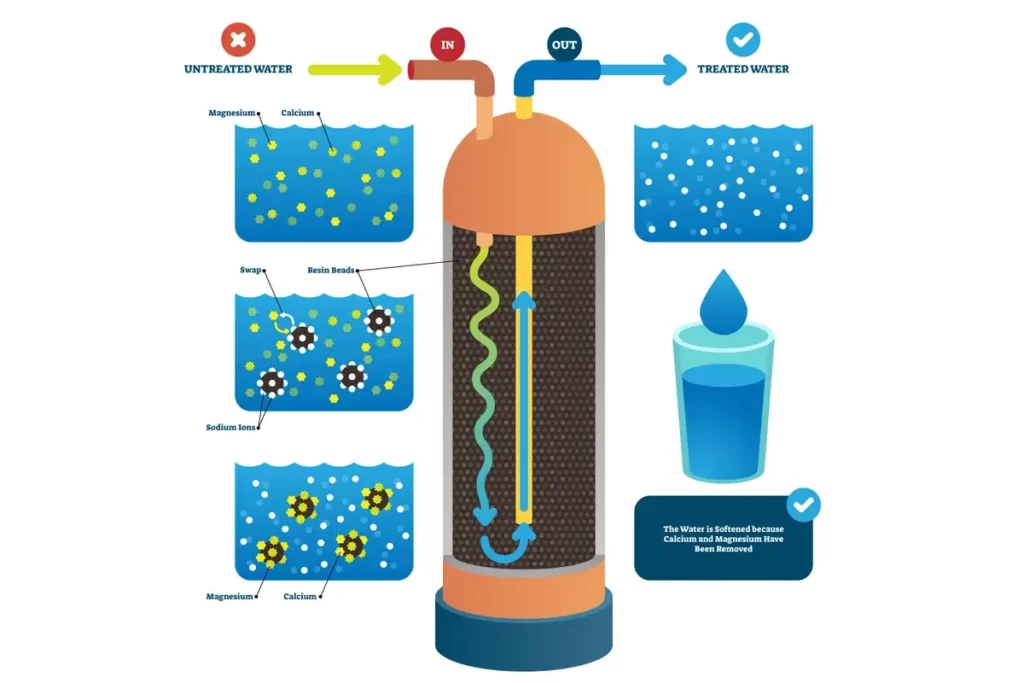
- Water Softening: Cation resins remove calcium and magnesium, softening hard water and protecting plumbing systems.
- Demineralization: Anion and cation resins are used together to remove both cations and anions for ultrapure water, ideal for industries such as pharmaceuticals and electronics.
- Desalination: In water desalination plants, ion exchange resins help remove salts from seawater, making it suitable for consumption and irrigation.
- Boiler Feed Water Treatment: Power plants and industrial facilities use ion exchange resins to remove impurities, reducing the risk of scaling and corrosion in boiler systems.
- Food and Beverage Processing: Ion exchange resins purify water used in beverage production, ensuring product quality and safety.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: These resins are critical for producing ultrapure water needed in drug manufacturing and laboratory use.